spring中的JdbcTemplate
环境:
Idea:2019.3.1
系统:windows10 家庭版
Jdk: 8
spring:5.0.3 release
spring文档
项目代码
1.概述
它是spring框架中提供的一个对象,是对原始Jdbc AOP对象的简单封装,spring框架为我们提供了很多的操作模板类。
操作关系型数据的:
JDBCTemplate
HibernateTemplate
操作Nosql数据库的
RedisTemplate
操作消息队列的:
JMSTemplate
JdbcTemplate在 spring-jdbc-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar 中,导入包的时候,除了这个jar包,还得导入一个和事务相关的包spring-tx-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar
2.使用
配置JdbcTemplate及数据源
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置jdbctemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myspringspace"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
使用JdbcTemplate插入账户数据
public class JdbcTemplateDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.获取JdbcTemplate对象
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate",JdbcTemplate.class);
//3.执行语句
jt.execute("insert into account(name,money)values('xxx',10000)");
}
}
3.实现curd操作
保存
jt.update("insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)","zzz",1000f);
更新
jt.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?","llll",20000f,8);
删除
jt.update("delete from account where id=?",9);
查询
查询所有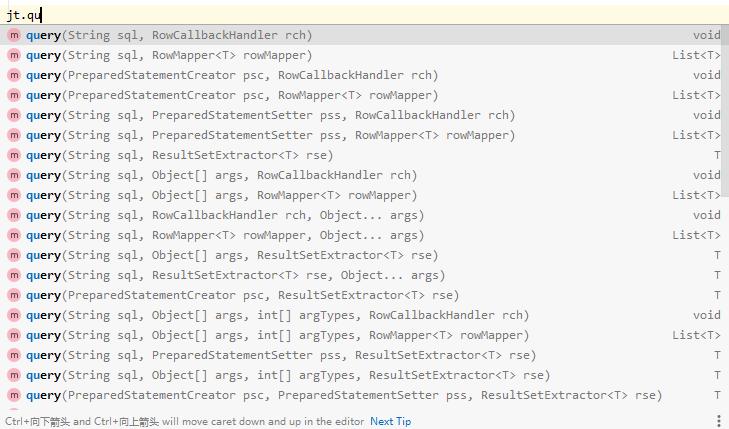
这是所有的query方法,但是并不是都能用到,我们通过2点来过滤
- 我们提供什么:sql语句,语句的参数
- 我们需要什么:返回一个List集合
根据这两点我们能定位到,只剩两个方法我们更适合去使用

这两个方法是针对不同的JDK版本使用的,第一个所有版本都能使用,第二个是JDK1.5之后才能使用,因为参数中有了可变参数
我们是JDK1.8所以能够使用第二种,这里我们使用第二种来查询
accountList = jt.query("select * from account where money=?", 第二个参数 ,1000f);
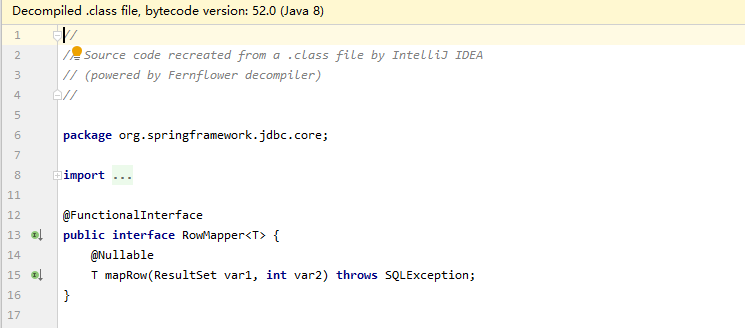
定位到RowMapper后发现,它是一个接口,所以我们要使用它的实现类来作为参数传入进方法
/**
* 定义account封装策略
*/
class AccountRowMapper implements RowMapper {
/**
* 把结果集中的数据封装到Account中,并由spring把每个Account加入到List集合中
*
* @param resultSet
* @param i
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public Object mapRow(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
//这里可以将Account的属性和表中的字段对应起来
Account account = new Account();
account.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
account.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
account.setMoney(resultSet.getFloat("money"));
return account;
}
}
完整的查询语句是这样的
List<Account> accountList = jt.query("select * from account where money>?",new AccountRowMapper(),1000f);
当然我们也可以使用spring为我们提供的RowMapper接口实现类BeanPropertyRowMapper<T>
//传入Account字节码
List<Account> accountList = jt.query("select * from account where money>?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),1000f);
类比一下dbutils中的QueryRunner中的query方法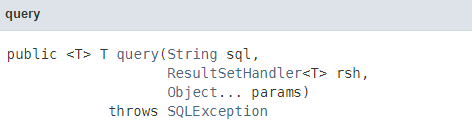
- QueryRunner.query:它的返回值类型是一个泛型,它的返回值类型是由ResultSethandler
中的返回值类型来觉得的 - JdbcTemplate.query:它的返回值类型是由不同的query方法来实现返回的,根据最开始截的那张query方法图能发现,有很多query方法,有参数不同的,有返回值不同的
查询一个
还是可以使用查询所有的方法
//传入Account字节码
List<Account> accountList = jt.query("select * from account where id=?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),1);
//取出查询结果
System.out.println(accountList.isEmpty() ? "没有内容" : accountList.get(0));
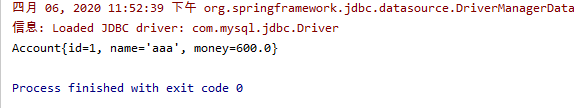
可以看到取出来id为1的账户
因为这一个方法可以满足查询任何情况,所以实际开发中也是使用这个方法
查询返回一行一列(使用聚合函数,但是不加group by字句)
//因为要返回一行一列,一行一列可以认为是一个数据,就像count(*)函数的结果,所以不能使用query方法,而是要使用queryForObject方法
//第二个参数填返回值类型的字节码,你传的什么类型的字节码,那么这个方法的返回值就是那个数据类型,我们使用的是long,所以我们用long来接受,int也可以,但是如果实际数据大于int的数据范围就会报错,所以实际上我们直接使用更大的long来接受
long count = jt.queryForObject("select count(*) from account where money>?",long.class,1000f);
System.out.println(count);
4.Jdbc的使用以及Dao的两种配置方式
刚刚是在main方法执行的语句,但是实际开发中,main方法一般是留给测试人员使用,我们应该将语句的执行放在dao层,我们新建dao层,创建IAccountServce接口,创建AccountServceImpl类,如下
AccountServiceImpl代码如下
import com.cbw.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.cbw.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl3 implements IAccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
List<Account> accountList = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id=?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
return accountList.isEmpty()?null:accountList.get(0);
}
public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) {
List<Account> accountList = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where name =?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountName);
return accountList.isEmpty()?null:accountList.get(0);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
}
试想一下,如果dao层实现类比较多,实际开发肯定不止这一个啊,那么我们每一个daoimp里面都有这段重复代码
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
新建一个JdbcDaoSupport类
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* 此类用于抽取dao中的重复代码
*/
public class JdbcDaoSupport {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate() {
return jdbcTemplate;
}
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
if(jdbcTemplate == null){
jdbcTemplate = createJdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
}
private JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
}
然后让accountDaoImpl类继承这个类,就只需要使用super关键子调用jdbcTemplate类了
import com.cbw.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.cbw.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements IAccountDao {
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
List<Account> accountList = super.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where id=?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
return accountList.isEmpty()?null:accountList.get(0);
}
public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) {
List<Account> accountList = super.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where name =?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountName);
return accountList.isEmpty()?null:accountList.get(0);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
super.getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
}
别忘了在xml文件中,配置accountDao,并在里面注入dataSource
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置账户的持久层-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.cbw.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myspringspace"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
执行测试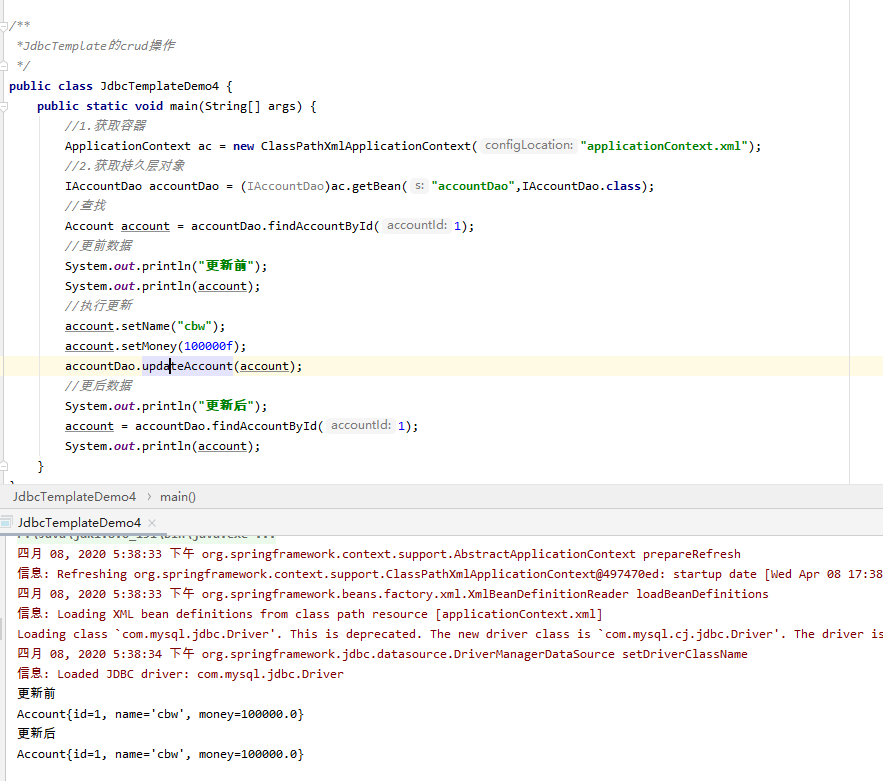
当然,spring中也给我们实现了这种方式,我们可以直接继承spring中的JdbcDaoSupport类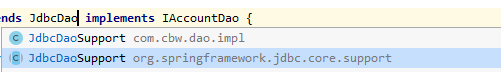
我们就不需要自己写support类,但是,这样写的话,我们就不能自己用注解配置jdbcTemplate了,因为那个是spring提供的jar包里面的,
所以,当我们使用继承spring中的JdbcDaoSupport类时,我们是使用xml配置dao的,当我们不使用这种方式,我们就可以使用注解方式来配置dao了,怎么选择看我们自己

